You’ve heard of ideas to cut carbon emissions through methods such as regulations, consumer changes, electric vehicles & more – but have you heard of methods to take the carbon straight out of the air itself? This new method of decarbonization is done through what is commonly known as “carbon capture tech”.
Carbon capture technology has emerged as a critical tool in the fight against climate change, offering a promising solution to reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), in the atmosphere.
What’s amazing about carbon capture tech is that it can reduce up to 14% of the global greenhouse gas emissions reductions needed by 2050.
What is Carbon Capture Tech?
Carbon capture is the system that relocates and recycles carbon dioxide in the environment. This emerging technology is the only verified method to remove emissions and greenhouse gases from the air.
Carbon capture technology, often referred to as carbon capture and storage (CCS), is a process designed to capture carbon dioxide emissions produced from the use of fossil fuels in electricity generation and industrial processes.
The objective is to prevent the release of large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, which has been the main contributor to the greenhouse effect and climate change.
The working principle of carbon capture technology involves capturing CO2 emissions at their source, typically from large point sources such as power plants and industrial facilities. Once captured, the CO2 is then transported and stored underground in geological formations, preventing its release into the atmosphere. This process is crucial in achieving significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and meeting global climate targets.
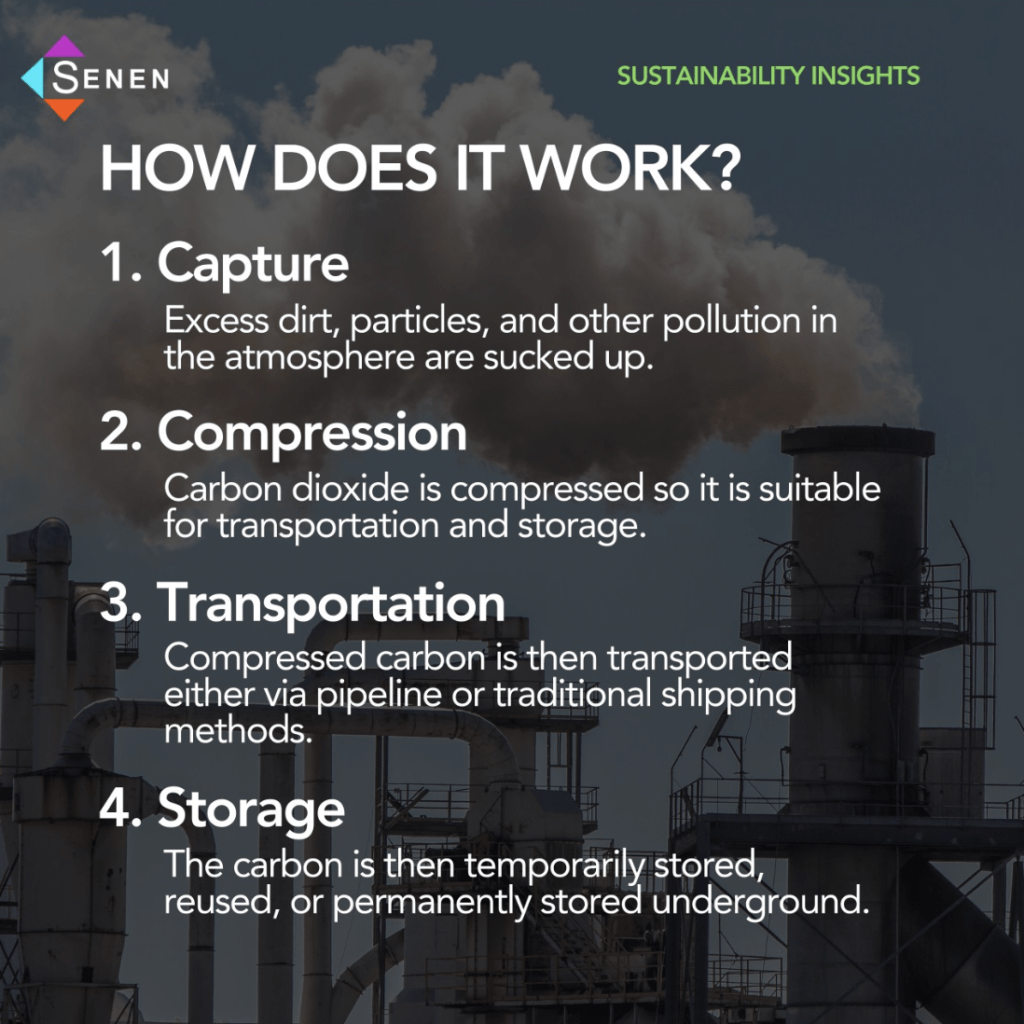
How Does it Work?
Carbon capture technology employs various complex methods to capture CO2 emissions. Here’s the general process of carbon capture:
- Capture: excess dirt, particles, and other pollution in the atmosphere are sucked up
- Compression: carbon dioxide is compressed so it is suitable for transportation and storage.
- Transportation: compressed carbon is then transported either via pipeline or traditional shipping methods.
- Storage: the carbon is then temporarily stored, reused, or permanently stored underground.
The Role of Data in Carbon Capture
Data plays a crucial role in the effective implementation of carbon capture technology.
Carbon capture storage (CCS) databases from CCS laboratories globally collect data about developing technologies, site evaluations, costs, and inventory to provide information to stakeholders, investors, and the general public.
Ex. the NETL’s CCS Database is presented using a Tableau Dashboard easily accessible on their website.
The monitoring, verification, and optimization of the entire process rely on accurate and real-time data. Here are several aspects that highlight the importance of data in carbon capture technology:
1. Monitoring and Control:
Data is used to monitor the performance of carbon capture systems, ensuring that the capture process is efficient and reliable. Sensors and monitoring devices collect data on factors such as CO2 concentration, temperature, pressure, and flow rates. This information is analyzed to identify any deviations from optimal conditions, allowing for prompt adjustments and maintenance.
2. Geological Storage Assessment:
Selecting suitable geological formations for the storage of captured CO2 requires extensive data analysis. Geophysical and geochemical data, along with geological models, are used to assess the potential storage sites. Factors such as rock permeability, porosity, and the presence of cap rocks are crucial considerations in determining the safety and effectiveness of storage locations.
3. Transportation Efficiency:
Efficient transportation of captured CO2 from the point of capture to storage sites is essential for the overall success of carbon capture technology. Data on transportation routes, infrastructure, and storage capacity are analyzed to optimize the logistics of CO2 transportation. This includes considerations for pipeline design, compression requirements, and safety protocols.
How is the Carbon Reused?
While the primary goal of carbon capture technology is to prevent the release of CO2 into the atmosphere, the captured carbon can also be put to beneficial use in various ways. Reusing captured carbon contributes to the concept of carbon utilization, turning a potential waste product into a valuable resource. Some approaches to reusing captured carbon include:
- Beverages: recycled carbon has been sold to companies like the Coca-Cola Company for preservation purposes.
- Clothing: clothes, sunglasses, and shoes can use carbon dioxide to create leather alternatives.
- Medical: captured carbon can be used in solvent consumption useful for pharmaceutical purposes.
- Buildings: carbon dioxide can be used to make concrete and other materials at a lower cost.
- Agriculture: carbon dioxide can be transformed into urea, a major ingredient in fertilizers.
- Furniture: carbon dioxide can be transformed into polyol, which is a key component in foams used for mattresses.
- Synthetic Fuels: CO2 can be converted into synthetic fuels through processes such as carbon capture and utilization (CCU) or power-to-gas (PtG).
- Carbon Mineralization: Carbon mineralization involves the conversion of CO2 into stable mineral forms through chemical reactions with minerals such as magnesium and calcium.
Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon capture technology stands as a crucial component in the global effort to combat climate change.
By preventing the release of large quantities of CO2 into the atmosphere, this technology plays a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The effectiveness of carbon capture technology relies on accurate data for monitoring, control, and decision-making throughout the entire process.
Moreover, the captured carbon opens up possibilities for innovative reuse, ranging from enhanced oil recovery to the production of valuable carbon-based products and synthetic fuels.
Ready to unlock your organization’s full potential? Contact us today and transform your organization’s data challenges into opportunities.


